Both corrective maintenance and emergency maintenance happen in response to a fault or issue with equipment. The main difference between the two is the scale of that problem.
Corrective maintenance identifies problems as a result of inspections, preventive maintenance (PM) tasks, or work orders. These issues typically do not affect the health or viability of a facility and its employees. On the other hand, emergency maintenance occurs when an equipment or facility problem significantly threatens safety, profitability, or the overall integrity of the institution.
A facility can’t usually avoid corrective maintenance because many small things can go wrong with any piece of equipment or space. For example, say a maintenance technician performs a routine inspection on a tenant’s room and finds a leaking pipe during that inspection. They will then perform corrective maintenance on the pipe as well, even though the initial inspection wasn’t concerned with the plumbing.
Unlike corrective maintenance, a facility can often eliminate most emergency maintenance scenarios with an effective PM program. This is because emergency maintenance only applies to the most significant maintenance needs. However, these threats can’t be completely eliminated, making an emergency maintenance plan a necessity for most, if not all, organizations.
Most facilities need both a corrective maintenance and an emergency maintenance program. However, there’s no need for both programs to be similarly specific or drawn out because corrective maintenance most often occurs during the course of other work (unplanned). Emergency maintenance programs should, for the safety and viability of a facility, be fleshed out as much as possible to avoid risk to employee and organizational health.
Differences between corrective and emergency maintenance
| Corrective maintenance | Emergency maintenance | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Corrective maintenance is work that takes place when issues are discovered during the course of another task like a PM or work order. | Emergency maintenance is a type of reactive maintenance aimed at preventing threats to a facility’s employees, property, or viability. |
| Workflow | 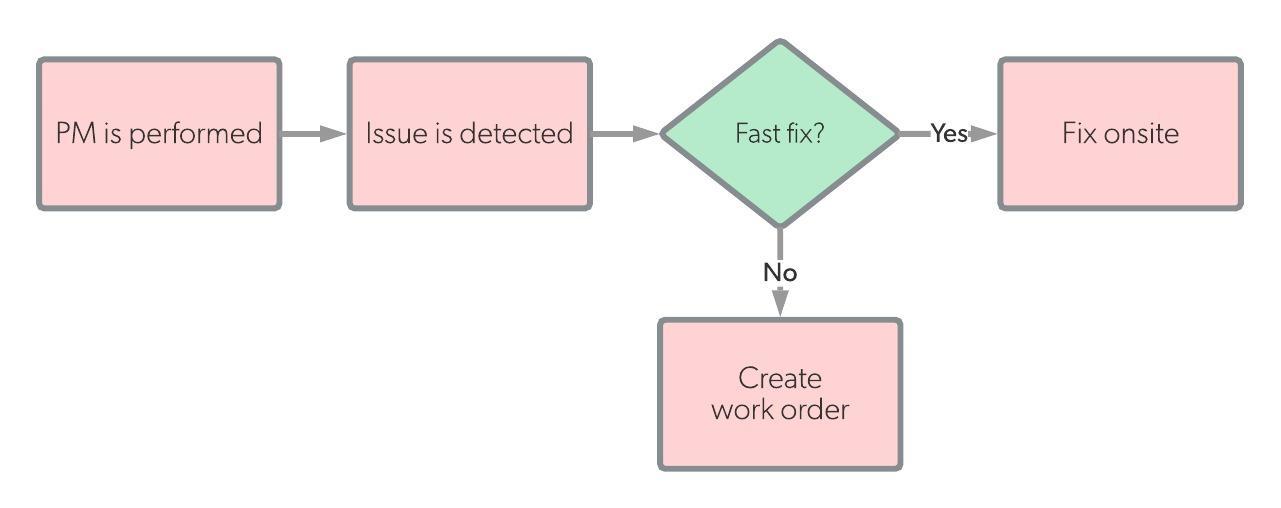 |
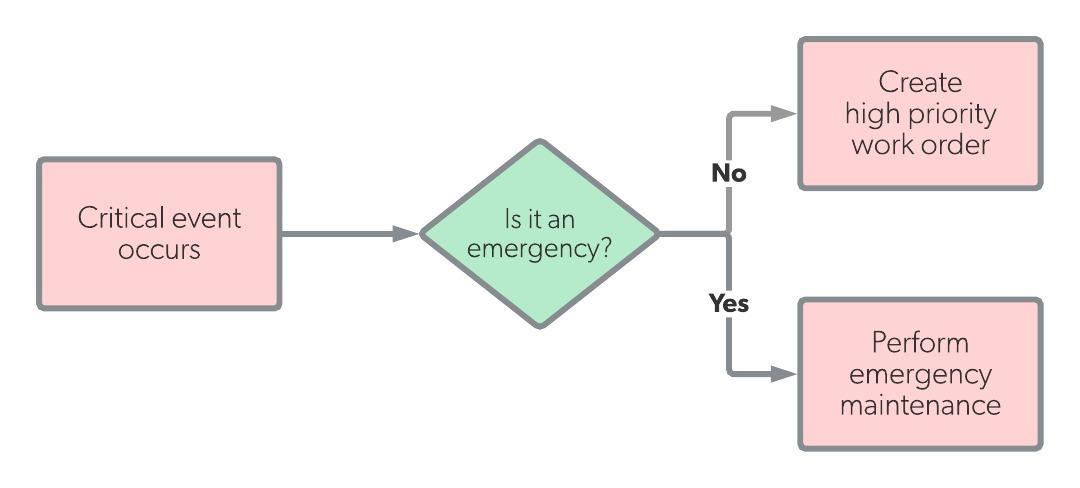 |
| Trigger | Discovery of issue | Automated trigger/response, human request |
| Cost | Low | Medium/High |
| Cost Savings | 10-30% [1] | Dependent on PM program effectiveness and types of possible emergencies |
| Resources Needed |
|
|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Use Case | An organization wants to decrease unplanned downtime and emergency maintenance but does not have a large maintenance budget. As a solution, they implement a PM program for select assets. Work orders are scheduled for inspections, lubrication, filter replacements, and parts replacements based on recommendations from OEMs. | A factory with a large variety of water piping creates an emergency maintenance plan for burst pipes. The need for the plan is clear as a burst pipe in a floor full of electrical equipment can be a significant health and profitability hazard for the organization and its employees. In tandem with this plan, the factory decides to further flesh out preventive maintenance inspections on the piping to lower the risk of an emergency occurring. |
[1] Christer Stenström, “Preventive and corrective maintenance – cost comparison and cost–benefit analysis.”


![[Review Badge] GetApp CMMS 2022 (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900459-get-app-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=347)
![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
